What is Contactless Access Control?
CIE's HowToAV takes a deep-dive look at the burgeoning trend for contactless, keyless and frictionless door entry and access control authentication methods.
What is contactless access control and door entry?
Contactless or touchless access control provides fast and secure access through doors, gateway & barriers, personnel turnstiles, etc without the need of physical contact such as fingerprint readers, keypads etc. Instead, contactless or frictionless door entry and access control methods such as biometrics, BLE, RFID and smartphone keyless entry are quickly becoming the entry options of choice.
Why is contactless access control important?
Post-covid, there is a strong reaction against the physical touching of devices, furniture etc in the workplace, leading to the latest architectural trends in 'contactless pathways'. There is also an increasing adoption of contactless as more technologies are integrated with our smartpones and devices are controlled from phone apps. Contactless is also about the user experience; people want things to be fast and easy and the only way to deliver this within access control is using fast, simple, contactless access control authentication methods.
What are the benefits of contactless access control?
- Reduces touch points at entry / exit locatgions which helps prevent spread of viruses and provides a more confident user experience
- Eliminates the need for person-to-person interaction in reception / lobbiy areas which can increase profitablility for businesses as less staff are needed for managing security of the building.
- Provides real-time data of building occupancy.
- No physical key capable or being lost or stolen.
- If your entry is via smartphone and you lose it, it is easy to block/cancel the ‘key’ on your lost device and re-assign to a new one.
- If using biometrics for entry - you are the key which cannot be lost. This also eliminates the need of physical keys and smart phone for entry.
- Remote access control - using cloud technology, allows you to both control and monitor access in homes from a remote location. You can add and remove access permissions, monitor and track access activity in your premises and lock/unlock the doors!
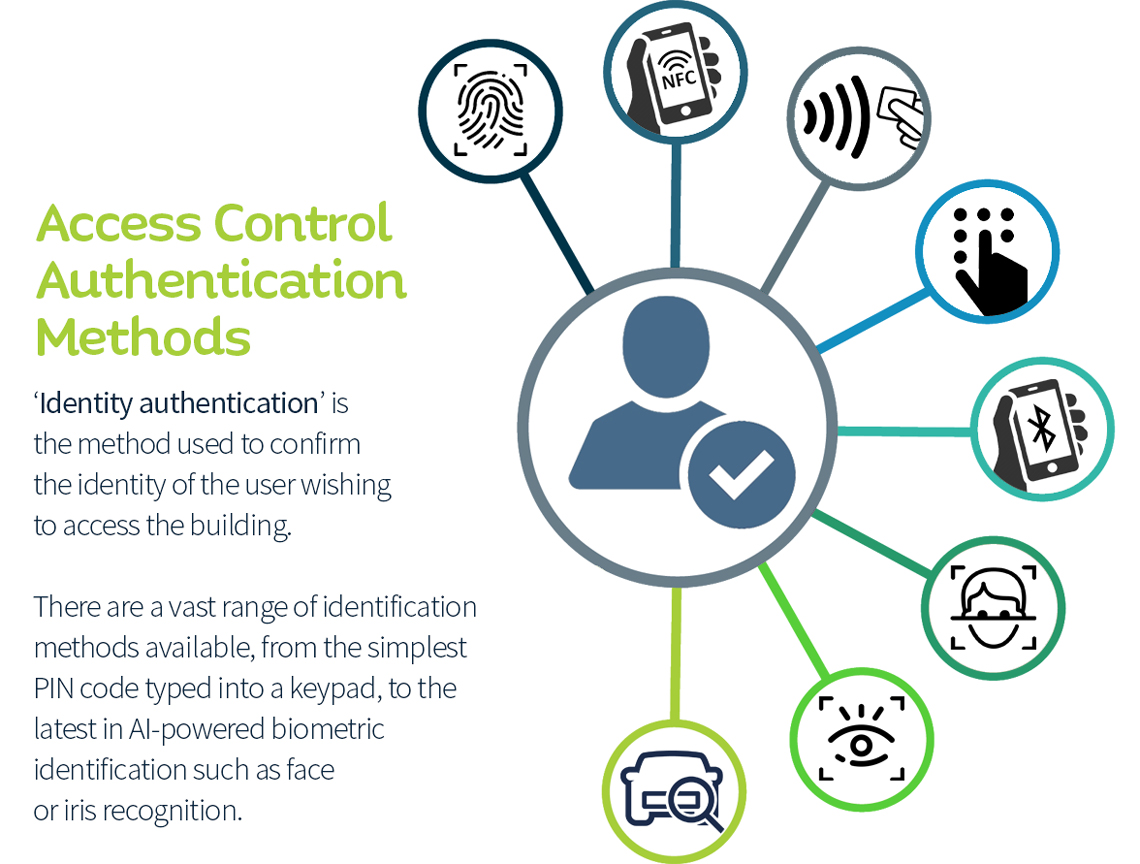
What contactless access control methods are there?
- RFID (keyfob or card)
- Bluetooth/BLE (smartphone)
- NFC (smartphone)
- Biometrics
- QR Code scanning (temporary key)
Click here for more details of access control identity authentication methods:
What is RFID access control?
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a wireless signal transmission technology frequently used in access control and door entry systems, which allows only authorised/registered users to enter secure spaces. RFID uses radio waves to read and capture data stored on tags (such as cards or key fobs) to provide unique information for the subject or individual.
.jpg)
What is BLE access control?
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) is also known as Bluetooth 4.0. When comparing Bluetooth Low Energy with standard Bluetooth, the main difference is in BLE’s low power consumption. With Bluetooth Low Energy's reduced power consumption, applications can run on a small battery for up to 5 years. This is vital for applications that only need to exchange small amounts of data periodically.
In Access Control applications, therefore, BLE helps to significantly increase the battery life for users' smart phones (compared with standard Bluetooth transmission).
In addition, as wireless, battery-powered access readers enter the market, Bluetooth Low Energy will become the transmission technology of choice for increased battery life.
Exactly the same as Bluetooth, BLE operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. However unlike original Bluetooth, BLE stays in rest mode until a connection is initiated. BLE’s actual connection time is a few mS, whereas Bluetooth takes around ~100mS. The reason the connections are short, is that the data rates are so high at 1 Mb/s.
An example of a Bluetooth-based mobile access control technology is 2N Wavekey.
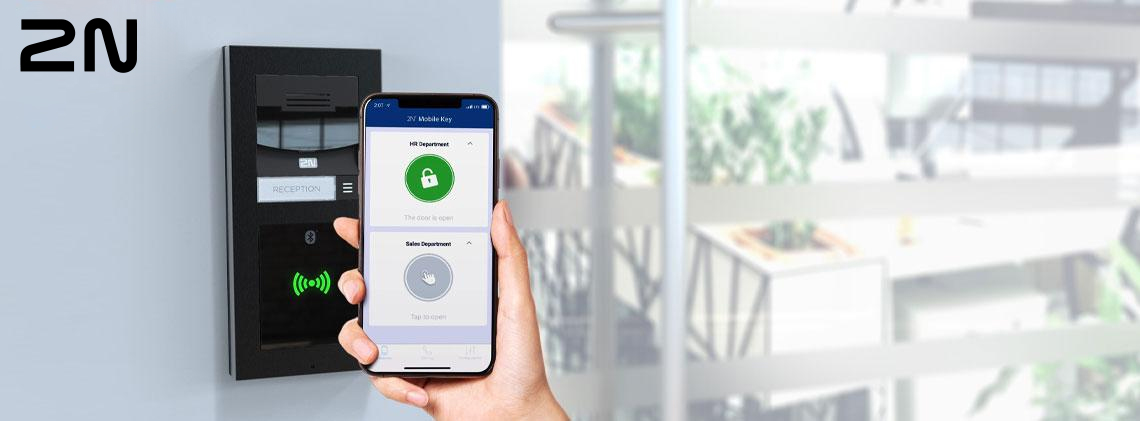

What is 2N Wavekey?
2N WaveKey is 2N's patented technology for mobile access control. 2N Wavekey allows security system administrators to generate and distribute access credentials to the user in a seconds, using a simple web interface and remote 'mobile key' distribution. There is no requirement to meet the user in person to provide physical credentials of keys. Wavekey stands out as it offers mobile credentials free of charge which are simple to distribute without the need for cloud connection.
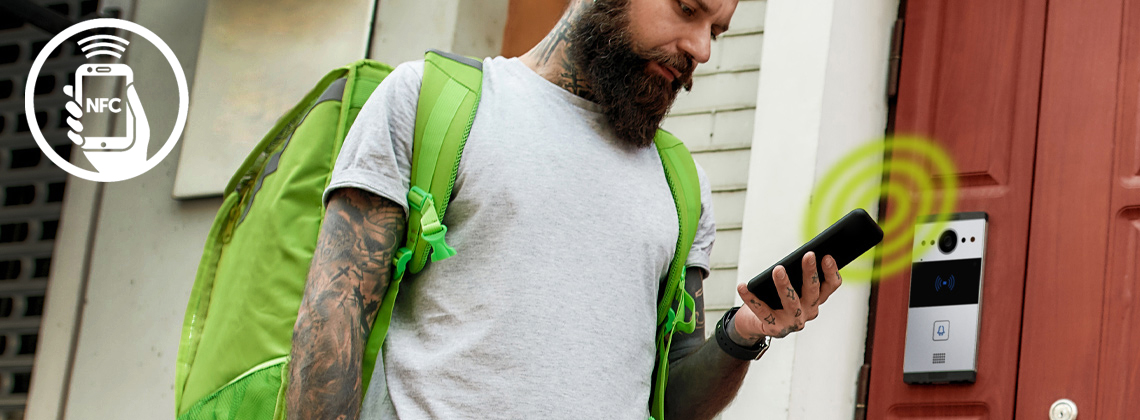
What is NFC access control?
NFC Access Control (Near Field Communication) allows for keyless and frictionless door entry using a smart phone device for authentication.
This short-range transmission radio frequency technology is a standard feature of most smart phones and is the same technology used for contactless payments from your phone or smart watch.
Access and Intercom system manufacturers are now incorporating NFC reader technology into access control and door intercom devices as a standard option as the trend for secure,convenient, wireless door unlocking becomes a growing requirement for residential and commercial users.

What is QR code access control?
QR Codes (Quick Response Codes) are similar to conventional bar codes, but are much more flexible and, due to their 2-dimensional structure, are able to hold much more data.
In the case of access control via QR codes, typically the entry system will include PC software or a smartphone app which can quickly and easily generate a unique QR code which can be set to allow access for a limited time period, specific days of the week, limited number of uses and entry limited to specific areas, floors or zones of the building.
Once the QR code has been generated, it can be emailed or messaged directly to the recipient (the user who requires temporary access to the building) for them to display on their smartphone device or print out if required.
A QR code-enabled Access Control or Door Intercom device will feature a scanner (in the form of a built-in camera); the user simply displays the received QR code from their smart phone to the access control device which will automatically scan it to confirm access rights within the specified time/usage criteria.

What is Biometric access control?
Biometrics use physical attributes of a person's unique identity this is typically fingerprints, retina scans, or facial scans. The main purpose of biometrics in access control is to verify someone's identity in order to prevent unauthorised people from accessing a building/area.
 |
Face Recognition – This form of biometric authentication uses a high resolution cameras and AI technology to scan each individual registered user’s unique facial features for identity verification. | |
 |
Iris Recognition Authentication – This form of biometric authentication uses a high resolution scanner for highly secure authentication via iris recognition. | |
 |
Fingerprint Scanning – This form of biometric authentication uses a finger print reader to confirm authentication via the users unique finger print. |
.jpg)
Find out more about Access Control and Door Intercoms:
-
What is Martyn's Law? exclusive interview with Figen Murray OBE
-
IFSEC Distributor Network - Ask the Security Experts
-
CIE adds Carson 24/7 remote concierge service to IP Intercoms
-
Tips for Access Control & Door Intercom system design
-
What is a Contactless Pathway?
-
The Ultimate Guide to Using Apple Wallet for Access Control
-
What is Bluetooth BLE Access Control?
-
What is a Door Entry System?
-
Keyless Door Entry Systems
Talk to the CIE team about Contactless Access Control and Door Entry SystemsIf you would like to discuss your next Access Control or Door Intercom system, please call the CIE sales team on T. 0115 9770075 or email [email protected].
|