What is 4K UHD?
HowToAV welcomes AV integration expert Neil Walton AV integration expert Neil Walton discusses in detail what 4K UHD / Ultra High Definition video content is, the different standards and the future of it.
AV integration expert Neil Walton dicusses 4K UHD / Ultra High Definition video content in a 4 part clikc the link below to watch part one.
Part one watch here
Are 4K and UHD (Ultra High Definition) video content the same thing are there differences?
4K video resolution provides much higher resolution video than 1080p (or HD) - increasing the number of pixels by 4 times.
As screens and televisions become larger, lower resolutions can deliver 'pixel blocking'; 4K UHD resolution recreates a cinematic experience with incredible visual detail.
What's the difference between 4K and UHD?
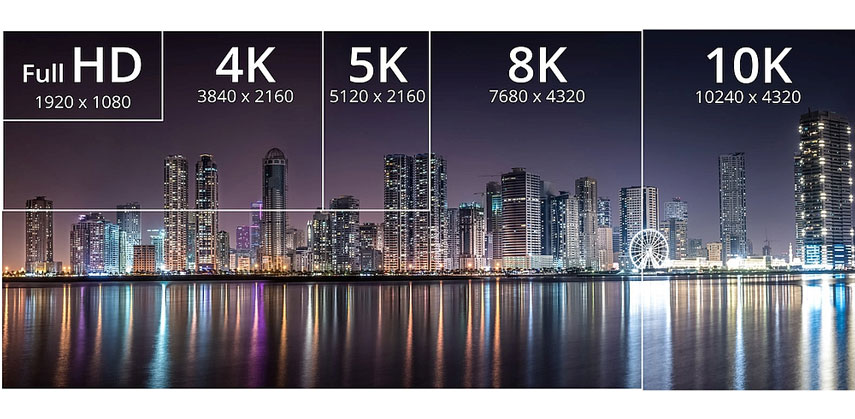
4K is in fact a cinematic resolution and display format (4096 x 2160 pixels)
UHD (or Ultra High Definition) is the residential screen/television resoltuion (3840 x 2160 pixels)
Part 2 watch here
Why have we gone with 4K UHD and not something bigger?
UHD has been chosen as a broadcast standard because it is a question of simple scaling. If you consider a 1080p image is actually a 1/4 of the size of the UHD image - UHD is twice as high and twice as wide as 1080p. 4K UHD means the TV's screen has a minimum resolution of 3,840 pixels wide and 2,160 pixels high.
 What should we be looking at when we're looking at 4K screens?
What should we be looking at when we're looking at 4K screens?
Frame rate - the number of frames or images that are displayed per second. Frame rates are used in synchronizing audio and pictures, whether film, television, or video. Frame rate is important because the more pictures you take per second the more data you capture which means you need greater bandwidth to deliver that signal.
Colour Spacing & Chroma Subsampling - Using something called Chroma subsampling you can reduce the amount of data you send. chroma sub-sampling is a common practice to encode video files using less resolution for chroma (aka color, as opposed to luma aka light).
In order to save precious megabytes (or sometimes gigabytes), it has been figured out that as long as you have the luma value for each pixel, you can then share the colour value between every four. Then you lose 75% of the colour information, hense some degradation, but still achieving acceptable quality of recordings. This type of encoding is chroma sub-sampling.
HDCP - the newest revision HDCP 2.2, protects 4K UHD content and - is a more secure protection protocol in order to protect all new content that the movie makers and TV production companies are currently investing in.
Part 3 watch here
What are the benefits of Higher Frame Rates?
The advantage of higher frame rates is you capture more data however, it also alleviates three major problems when filming:
- Motion blur
- Strobing
- Large Area Flicker
Why is colour spacing important?
When you're delivering an HDMI signal like UHD resolution and higher frame rates there is lots of data and we are limited to the transmission of this data by the cables or transmission system used. So there is a technology that has been released called 420 colour subsampling. Every pixel on a screen has 2 attributes/values one is, its 'Luma Value' which is how black and white the pixel is which gives you the detail. The other value is 'Chroma Value' which is the colour it is. If you remove the chrome of data from an image you end up with a black and white image. If you remove the luma value you get no image because you've got no detail. Because the human eyes are a lot more sensitive to black and white and colour you can cheat on the colour spacing. You can share colour across pixels, so although we see the detail we don't notice that some should have their own individual colour and that they actually share and spread colour across more than 1 pixel, now we're using something called 420 Colour Subsampling.
What is 420 Colour subsampling?
When you reduce the amount of chroma to 50%, this is important because we need to deliver HDMI signals across HDBaseT and HDBaseT has a maximum delivery speed of 8 gigabits per second. If something is filmed using full colour 4:4:4 and not sub sampled there is too much data - so by using 420 Colour Subsampling that's reducing the data by about half. This means you are now below the maximum bandwidth speed of HDBaseT and can now deliver high frame rate image at UHD with the 420 Colour Subsampling.
 What is Motion Blur?
What is Motion Blur?
Motion Blur occurs for example if you are filming a football game, when there is a ball that goes across the camera and it looks blurred. It is also very similar to when you are capturing a photo and the camera jars at the last second you capture the photo which is then blurred. To alleviate this what they tend to do is to reduce the shutter speed when taking these pictures - so they take the same amount of pictures per second but with very short ones.
What is Strobing?
Where it looks as if (using the football example again), the ball has jumped across the screen. By increasing the frame rate and increasing the number of pictures taken per second you alleviate both motion blur and strobing problems.
What is Large Area Flicker?
This occurs on your peripheral vision on big screens and bright areas where the bright picture fuses and frame rate, once again by increasing frame rate you can reduce that.
Part 4 watch here
What sources can I plug into my 4K UHD Television?
- Sony 4K Media Streamer
- Amazon 4K Media Streamer
- BT Sport UHD
- Netflix Media Streamer
- In the commercial market - digital signage players that are 4K, this is where you will probably see the benefit of 4K the most.
- In the near future 4K Blu-ray players - this will probably drive the market even more because a lot of the other products rely on bandwidth because you have to stream the content. Where as once you can buy a product like 4K Blue-ray player, you can then own 4K content.
What do you think the future is for display standards?
HDR - High Dynamic Range: a way of presenting video with more luminance, more contrast and more colours.
8K - "Something in the future I think will develop with 8K."
HD- 10K display standards
What is 8K?
4K footage has 8 megapixels 8K triples this, which takes displays up to a full 32 megapixels per frame. Meaning that we will get a display resolution of 8K horizontally and 6K vertically – for viewers with 20/20 vision, this creates a resolution that is technically perfect. Beyond this, we are incapable of perceiving much more detail, putting us on a scale of ever diminishing returns.
 Want help with your next AV project?
Want help with your next AV project?
CIE is one of the UK's leading and most innovative professional AV distributors and is a leading provider of AV signal and HDBaseT professional systems and devices.
With over 50 years experience in supply and system design for many of the UK's largest, high profile audio projects, our AV experts provide a unique level of technical support and customer service.
Call the CIE AV experts now on T. 0115 9770075 or email us at [email protected]
 Got a question for CIE's HowToAV team?..
Got a question for CIE's HowToAV team?..
HowToAV.tv provides a whole host of tips, tricks and technology know-how for the professional audio visual industry.
If you have a question for our AV experts, please contact us now.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel now at howtoav.tv for all the latest video casts or send us your questions to [email protected]
Featured Products











